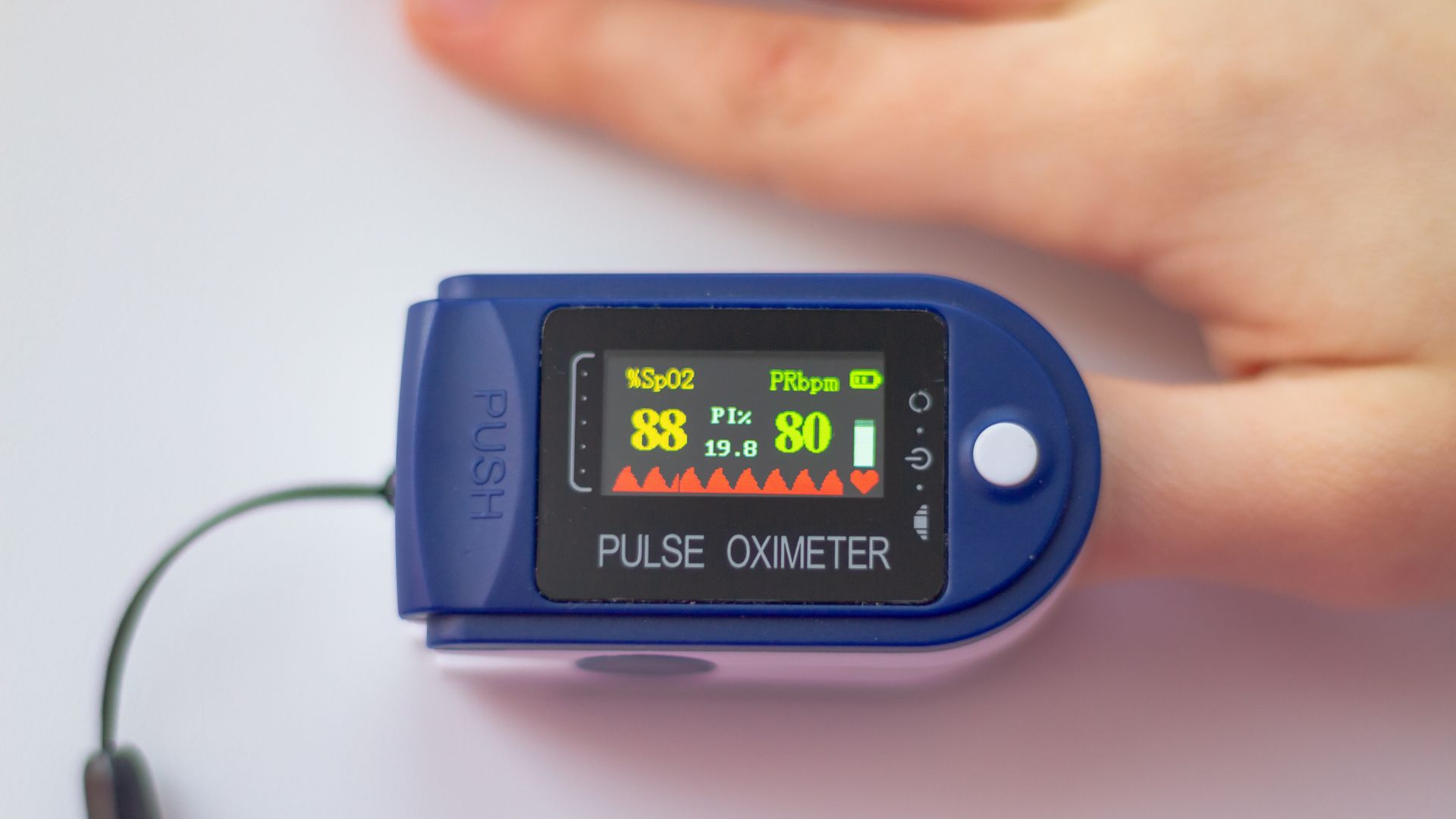
As a doctor, I often stress the importance of oxygen to my patients. It’s something we take for granted – until there’s not enough of it. Oxygen is the fuel that keeps our bodies running, and when we don’t get enough, the consequences can be severe. If you’ve ever wondered what happens when your body lacks oxygen, also known as hypoxia, let’s dive into the dangers, symptoms, and ways to prevent it.
Learn More: Master CoQ10 (Ubiquinone) – Achieve Cardiovascular & Immune Wellness
Why Is Oxygen Important for the Body?
Oxygen is essential for every cell in our body. It fuels the process of converting food into energy, ensuring that our organs and tissues function properly. Without sufficient oxygen, our cells begin to suffer, and over time, this can lead to serious health issues. The brain, heart, and other vital organs depend on a constant oxygen supply to work efficiently.
Causes of Low Oxygen Levels (Hypoxia)
Hypoxia can be caused by several factors, including:
- Respiratory Diseases: Conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pneumonia, and COVID-19 can restrict oxygen intake.
- Heart Problems: Cardiovascular diseases, heart failure, and blocked arteries can limit oxygen-rich blood from reaching vital organs.
- Anemia: A lack of red blood cells reduces the body’s ability to transport oxygen.
- Altitude Sickness: High altitudes have lower oxygen levels, leading to altitude sickness in those not acclimated.
- Obstructed Airways: Choking, drowning, or an allergic reaction can physically block oxygen from entering the lungs.
- Sleep Apnea: This condition interrupts breathing during sleep, reducing oxygen intake over time.
Symptoms of Low Oxygen Levels
Your body gives warning signs when it’s not getting enough oxygen. The symptoms of hypoxia include:
- Shortness of breath, even with minimal activity
- Rapid heartbeat (tachycardia)
- Dizziness and lightheadedness
- Confusion and difficulty concentrating
- Bluish tint on lips or fingertips (cyanosis)
- Fatigue and weakness
- Chest pain in severe cases
If you experience any of these symptoms, especially in combination, it’s crucial to seek medical attention immediately.
Dangers of Oxygen Deprivation
The long-term effects of hypoxia depend on its severity and duration. Some of the major risks include:
- Brain Damage: The brain is highly sensitive to oxygen deprivation. A few minutes without oxygen can lead to irreversible brain injury.
- Heart Problems: The heart works harder to compensate for low oxygen, increasing the risk of heart failure and arrhythmias.
- Organ Failure: Prolonged oxygen deficiency can damage the kidneys, liver, and other organs.
- Coma or Death: In extreme cases, lack of oxygen can result in loss of consciousness and even death if not treated promptly.
Preventing Hypoxia and Maintaining Healthy Oxygen Levels
While some causes of hypoxia are unavoidable, there are steps you can take to maintain healthy oxygen levels:
- Exercise Regularly: Cardiovascular exercise strengthens the lungs and improves oxygen circulation.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking damages lung tissue, reducing oxygen absorption.
- Monitor Air Quality: Poor air quality can affect breathing; consider using an air purifier if necessary.
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration helps the blood transport oxygen efficiently.
- Practice Breathing Techniques: Deep breathing exercises, such as diaphragmatic breathing, can improve lung function.
- Seek Treatment for Underlying Conditions: If you have asthma, COPD, or another respiratory disease, follow your doctor’s advice to manage symptoms and improve oxygen intake.
Learn More: Master CoQ10 (Ubiquinone) – Achieve Cardiovascular & Immune Wellness
Final Thoughts
Oxygen is life, and ensuring your body gets enough of it is essential for overall health. If you ever feel breathless, fatigued, or confused without explanation, don’t ignore these signs—your body might be warning you about low oxygen levels. Seeking medical advice early can prevent serious complications and help you maintain optimal health.
Have any questions or personal experiences with low oxygen levels? Let’s discuss them below!